

![]() [1] Digital Certificates [2] are issued by a Certificate Authority [CA]. Any organisation can opt to operate its own CA and typically the types of organisations that have a CA are either commercial CAs that offers their services to other organisations as an external service, or organisations that purchase the necessary systems for their own use.
[1] Digital Certificates [2] are issued by a Certificate Authority [CA]. Any organisation can opt to operate its own CA and typically the types of organisations that have a CA are either commercial CAs that offers their services to other organisations as an external service, or organisations that purchase the necessary systems for their own use.
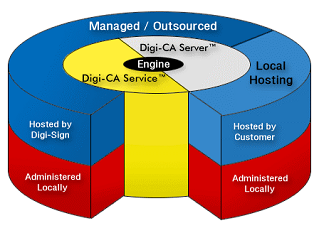
The computer system that issues the different types of Digital Certificate does this from the central system core of the CA system and this core is called the Certificate Engine.
Regardless of the type of CA system or how it is operated, the Certificate Engine for the system has at least one Root Certificate. The Certificate Engine core uses the Root Certificate to sign the various types of Digital Certificates the CA issues.
Links:
[1] https://www.digi-sign.com/downloads/download.php?id=digi-ca-pdf
[2] https://www.digi-sign.com/en/digital+certificate
[3] https://www.digi-sign.com/compliance/introduction
[4] https://www.digi-sign.com/trust+centre
[5] https://www.digi-sign.com/demos/aacd